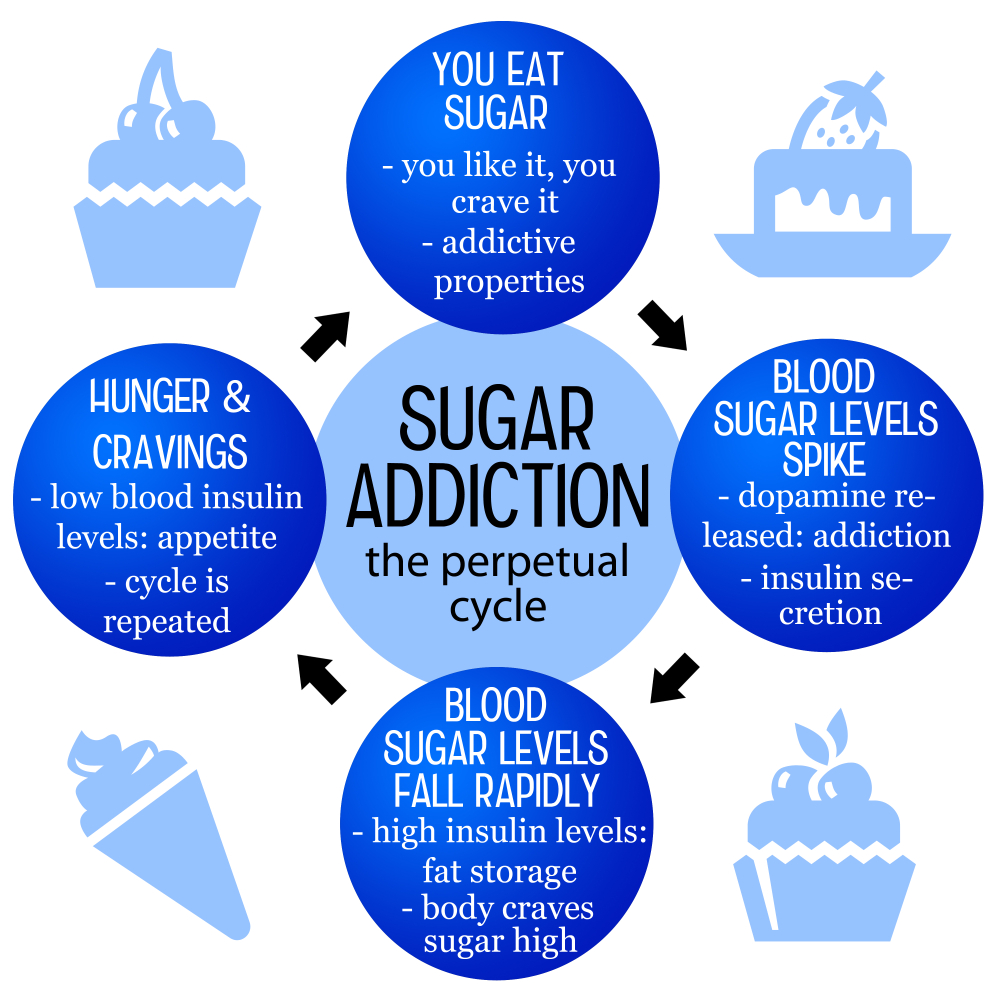
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked extensive debate among nutritionists and health experts alike. Many individuals experience intense sugar cravings, indicating a potential form of sugar addiction, which may lead to compulsive eating behaviors and increased health risks of sugar consumption. With the rise of added sugar in our diets, understanding the effects of sugar on our bodies has never been more crucial. This inquiry delves into the complex relationship between sugar and addiction, shedding light on the psychological and physiological impacts that excessive sugar intake may have on overall health.
Exploring whether sugar can be classified as addictive raises a multitude of questions about our dietary habits. The desire for sweet flavors often manifests in repeated consumption, leading to what many refer to as sugar dependency or cravings. This phenomenon brings to light the broader implications of added sugars in our food environment, as they often exacerbate unhealthy eating patterns. With insights into the potential health consequences tied to high sugar intake, it becomes essential to examine the role of sugar in our diets and its psychological impact. This discussion not only addresses the addictive qualities of sugar but also prompts a reevaluation of how we perceive our cravings for sweets.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a contentious topic among healthcare professionals and nutritionists. While sugar does not fit the strict clinical definitions of addiction that substances like nicotine and opiates do, it can certainly induce cravings and compulsive behaviors in some individuals. The palatable nature of sugar, particularly in ultra-processed foods, often leads to habitual consumption. As people indulge in sugary snacks or beverages regularly, their bodies can start to crave these items, leading to what many describe as addiction-like behaviors.
Research suggests that the average American consumes far more added sugar than recommended, reaching nearly 20 teaspoons a day, primarily through sugary drinks and snacks. This excessive consumption can result in withdrawal-like symptoms—headaches, anxiety, and dizziness—when individuals attempt to cut back. The psychological effects of craving sugar can be significant, impacting not only physical health but also emotional well-being. Therefore, it’s crucial to distinguish between the need for natural sugars in fruits and vegetables, which are vital for health, and the detrimental effects of added sugars.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
Consuming high amounts of added sugars can lead to various health risks including obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Studies have shown that excessive intake of sugar, particularly from sugary beverages, significantly correlates with weight gain and metabolic disorders. These health risks are compounded by the fact that most processed foods not only contain high sugar levels but also unhealthy fats and sodium, further increasing their negative impact on health. As such, moderation in sugar consumption is essential to maintain optimal health and well-being.
In addition to physical health issues, the psychological effects of sugar consumption should not be overlooked. Increased sugar intake can create a cycle of cravings and compulsions that mimic addictive behaviors. This cycle can lead to emotional eating and even mood swings, making it difficult for individuals to control their intake. Understanding the effects of sugar on health is crucial for making informed dietary choices and developing healthier eating habits.
Health Risks Associated with Excess Sugar Consumption
The health risks associated with excessive sugar consumption go beyond just weight gain. High intake of added sugars is directly linked to an increased risk of heart disease, as it can lead to inflammation, high blood pressure, and elevated blood lipids. Moreover, sugar-sweetened beverages contribute significantly to dental problems like cavities and erosion due to their high acidity levels. It’s important to consider these long-term health implications when assessing our sugar consumption habits.
Another critical issue related to sugar consumption is its impact on mental health. Research indicates that high sugar diets can be associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety. The repetitive cycle of indulging in sugar and experiencing a subsequent sugar crash can lead to significant mood fluctuations. Hence, limiting added sugar intake not only promotes physical health but can also contribute to better mental resilience.
Managing Sugar Cravings Effectively
Managing sugar cravings is a challenge many face, especially in a society where sugary snacks are prevalent. One effective strategy is to gradually reduce added sugar consumption rather than going cold turkey. This approach can help minimize withdrawal-like symptoms and cravings. Instead, individuals can opt for natural sweeteners or whole foods containing sugars, such as fruits and yogurt, which provide essential nutrients along with sweetness.
Additionally, understanding the triggers for sugar cravings can assist in managing them effectively. Stress, boredom, and even lack of sleep can increase the urge to reach for sugary snacks. By addressing these root causes—whether through stress-relief techniques, regular exercise, or maintaining a balanced diet—individuals can reduce their likelihood of turning to sugar for comfort.
Recognizing Added Sugar in Your Diet
An essential step in managing sugar intake is to become adept at recognizing added sugars in various food products. Food labels can often be misleading, with many items marketed as ‘healthy’ still containing high levels of added sugars. Familiarizing oneself with ingredient lists and recognizing terms such as sucrose, fructose, and corn syrup is crucial in making informed dietary choices.
Moreover, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods is an excellent way to minimize added sugar consumption. Whole fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contain natural sugars along with fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Incorporating these foods into daily meals not only satisfies sweet cravings in a healthier way but also provides significant health benefits, helping to mitigate the risks associated with high added sugar intake.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
While there are significant concerns about sugar consumption, it’s crucial to acknowledge that sugar does play a role in a balanced diet. Naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and vegetables provide essential nutrients and energy. The focus should be on limiting added sugars, which contribute nothing but empty calories. By prioritizing whole foods, individuals can enjoy the sweetness of natural sugars while maintaining a healthy overall diet.
Finding a balance between enjoying the sweetness that sugar provides while maintaining health is key. Recognizing that not all sugars are created equal, and that moderation is vital can help individuals enjoy their favorite treats without excessive health risks. Clinicians emphasize that sugar should be consumed mindfully—celebrating its role in our diets while being aware of the potential health consequences of overindulgence.
Changing Habits to Reduce Sugar Intake
Changing established habits around sugar consumption is crucial for healthier living. To make lasting changes, individuals can start by setting realistic goals, such as reducing sugar intake gradually rather than eliminating it completely. Gradual reduction helps the body adjust to lower sugar levels and lessens cravings. Keeping track of daily sugar intake can also provide insights into habitual consumption and encourage more mindful eating.
Another helpful strategy includes substituting sugary snacks with healthier options like nuts, yogurt, or fruit. This not only helps satisfy a sweet tooth but also provides beneficial nutrients. Engaging in mindful eating practices, such as savoring each bite and paying attention to hunger cues, can foster a healthier relationship with food, promoting long-term changes in dietary habits.
Education on Sugar Consumption
Education plays a vital role in understanding sugar consumption and its effects on health. Individuals must be informed about the recommended daily intake of sugar and familiarize themselves with reading food labels effectively. Nutrition programs and resources can provide the groundwork for understanding how much added sugar one consumes and the health ramifications associated with it.
Moreover, public health campaigns targeting sugar consumption can help raise awareness about the need to limit added sugars. This can lead to more informed choices in both personal and community health practices. By championing positive changes in dietary habits through education, individuals can better manage their sugar intake and promote overall health.
The Future of Sugar Consumption Patterns
As society grows increasingly aware of the health risks associated with high sugar consumption, shifting patterns in sugar intake are expected to emerge. There is a growing trend towards more health-conscious choices, with consumers becoming more vigilant about the nutritional content of their food. This increased awareness can motivate manufacturers to produce healthier products with less added sugar.
The future might also see a rise in the popularity of alternative sweeteners and healthier snack options as individuals seek to satisfy their sweet cravings in healthier ways. As awareness of sugar addiction and its related health risks compounds, societal shifts towards healthier eating patterns are anticipated, ultimately leading to improved public health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive and what are the implications of sugar addiction?
Sugar is often debated in terms of its addictive qualities. While it’s not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, it can lead to increased cravings and compulsive behaviors due to its prevalence in ultra-processed foods. Understanding sugar addiction is essential, particularly regarding how excessive sugar consumption can impact health.
What are the health risks of sugar addiction?
The health risks associated with sugar addiction are significant, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Excessive added sugar consumption can lead to serious health consequences. Therefore, it’s crucial to monitor sugar intake and aim for the recommended limits set by health organizations.
How do sugar cravings relate to sugar addiction?
Sugar cravings are closely linked to sugar addiction. When individuals consume high amounts of sugar, their bodies may become accustomed to it, leading to cravings when they attempt to reduce their intake. Recognizing sugar cravings can help in understanding the psychological aspects of sugar addiction.
What are the effects of sugar and how do they contribute to sugar addiction?
The effects of sugar include increased dopamine levels in the brain, which can foster feelings of pleasure, making sugary foods highly palatable. This cycle can contribute to habitual consumption, resembling addictive behaviors, even though sugar isn’t officially classified as an addictive substance.
How should I manage added sugar consumption to avoid sugar addiction?
To manage added sugar consumption and avoid sugar addiction, it’s advised to gradually reduce intake rather than going cold turkey. Reading food labels and being mindful of what you consume can help maintain a healthy balance, lowering the risk of dependency on sugary foods.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Addictiveness of Sugar | Sugar increases cravings and can lead to compulsive eating, but is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Comparison with Other Addictive Substances | Withdrawal symptoms from sugar are not as severe as those from alcohol or drugs, but can include headaches, dizziness, and anxiety. |
| Sugar in Diet | While sugar has addictive qualities, it’s necessary for survival in the form of fruits, vegetables, and dairy. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association recommends 6-9 teaspoons of added sugar per day, far less than the average American intake of around 20 teaspoons. |
| Impact of Reducing Sugar | Sudden elimination of sugar can lead to cravings; gradual reduction is advisable. |
| Role of Sugar | Moderate sugar consumption can enhance food enjoyment and is essential in our diets. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked significant debate in the health community. While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive consumption, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like substances such as alcohol or nicotine. Understanding the role of sugar in our diet is crucial; it not only provides taste and satisfaction but is also necessary for our nutritional well-being. The key takeaway is moderation—recognizing how much added sugar we consume each day and adjusting our diets accordingly can help mitigate the risks associated with high sugar intake. Thus, while sugar has some addictive properties, it should be distinguished from traditional addictive substances.