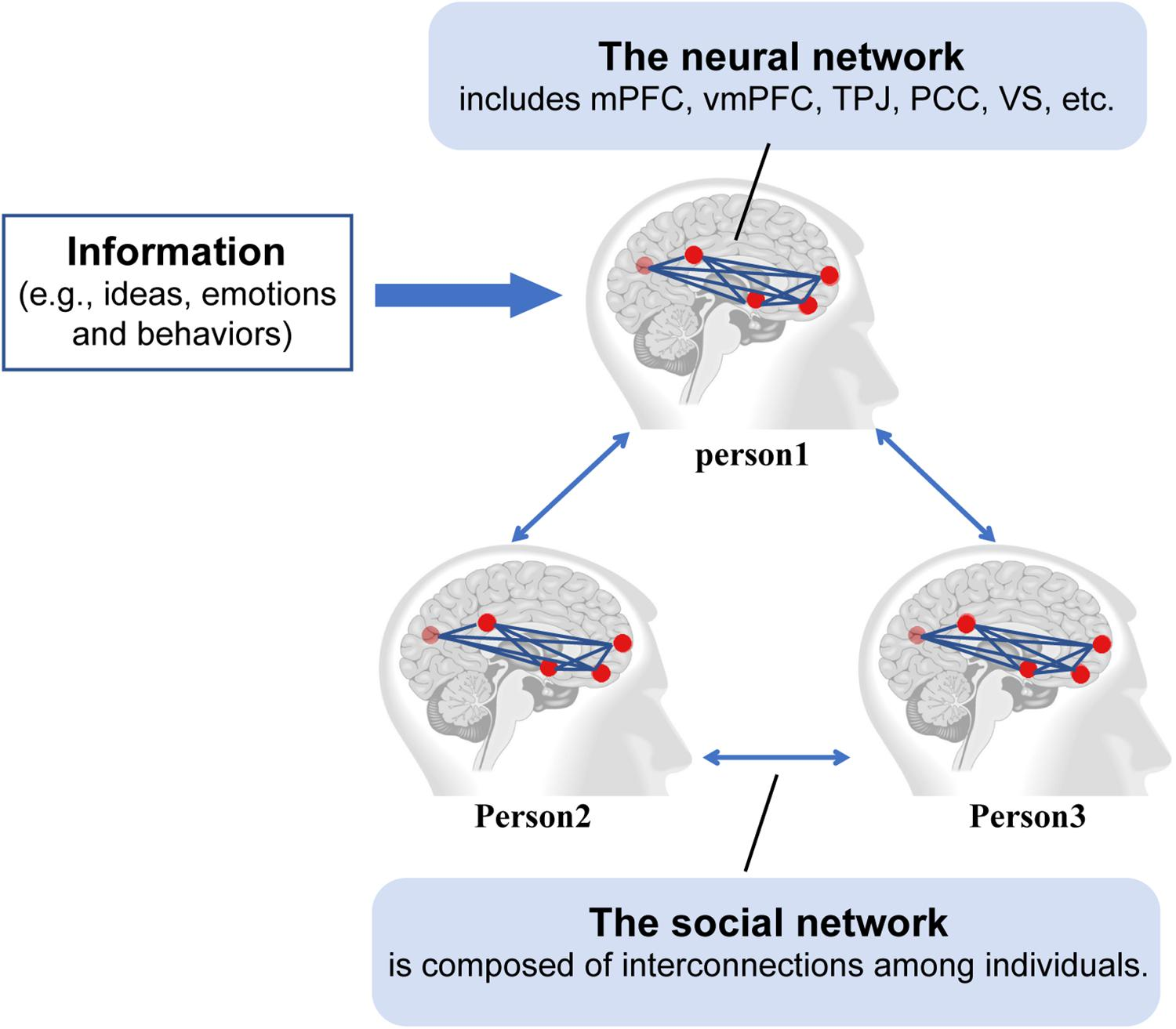
Social connection neuroscience is a fascinating field that explores the intricate relationship between our brains and the need for interpersonal relationships. As health professionals increasingly recognize the importance of social connection for mental health, researchers are uncovering the neural mechanisms behind social interactions. The neuroscience of social interaction reveals how our brains are wired to seek out companionship, impacting our emotional well-being and social behavior. Understanding these neurological pathways is crucial, especially given the alarming effects of social isolation on mental health and social needs. By shedding light on the importance of social connection, this research not only highlights the role of social bonds but also emphasizes the consequences of disconnecting from others.
Exploring the neural foundations of social interaction opens up a dialogue about the critical role of relationship-building in our lives. Terms such as social behavior and brain connectivity feature prominently in discussions around how humans engage with one another. Researchers are investigating the mechanisms that dictate our social needs, which can significantly shape our mental well-being. The exploration of these interactions sheds light on how both positive engagements and negative experiences, such as loneliness, can influence our psychological state. In this light, comprehending the effects of social isolation becomes vital for promoting healthier relationships and better mental health outcomes.
The Neuroscience of Social Connection
Recent findings in neuroscience have illuminated the complexity of social connection as an essential element of human life, similar to the need for food, water, and shelter. Researchers have been delving into the neural pathways that govern our desire for social interactions, uncovering how the brain encodes these needs. The 2023 report by the U.S. Surgeon General emphasizing social isolation as a public health crisis underscores the growing recognition of how vital social connections are for mental wellness and overall health. Through these studies, it is becoming increasingly clear that the neuroscience of social interaction plays a pivotal role in understanding our mental health needs.
The exploration of social connection neuroscience highlights how intertwined social behavior is with neurological functions. In particular, the research discusses the hypothalamic circuit that regulates social homeostasis, demonstrating that our brains are wired to crave social interactions in a manner akin to meeting basic physiological needs. Liu’s work illustrates that our desire for social contact may stem from an underlying biological imperative, echoing the approaches taken in hunger and thirst research. This shifting perspective not only pushes the boundaries of neuroscience but also emphasizes the importance of fostering social connections for maintaining both psychological and physical health.
The Importance of Social Connection in Mental Health
Understanding the significance of social connection extends far beyond mere companionship; it delves into the realm of mental health. Social isolation has been linked to various psychological issues, such as anxiety, depression, and even severe conditions like schizophrenia. Liu’s research not only establishes a biological basis for social needs but also highlights that engaging socially is fundamental to mitigating mental health challenges. As individuals face the growing threat of social isolation in an increasingly digital world, the necessity of fostering real-world connections is underscored.
The importance of social connection for mental health has profound implications for designing effective interventions. Mental health professionals are called upon to consider the social needs of their patients, emphasizing the advantages of group therapies and social activities as significant avenues for recovery. Moreover, recognizing that the brain’s response to social deprivation is similar to that of other basic needs can inform targeted strategies to alleviate feelings of loneliness. Thus, promoting social wellness emerges as an essential aspect of comprehensive mental health care.
The Effects of Social Isolation on Brain Function
Social isolation can lead to significant consequences not just on an emotional level but biologically, affecting brain function and our mental health trajectory. Liu and his team discovered that prolonged periods of social deprivation could result in an aversion to social activities, indicating the brain’s response to excessive isolation may be counterproductive. Their findings point to the adaptability of the brain’s social circuits – when deprived of social contact, the neural mechanisms that normally facilitate social behavior can become impaired.
Additionally, the research suggests that sensory inputs play a crucial role in fulfilling social needs. The experiments conducted revealed that mere visual or auditory exposure to social stimuli is insufficient to mitigate feelings of loneliness; tangible touch seems indispensable. Recognizing how sensory experiences influence social behaviors can guide future studies aimed at developing approaches to combat the detrimental effects of social isolation. This understanding is not just theoretical; it has real-world repercussions for those who might be suffering from isolation due to circumstances like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Social Behavior and the Brain: Connections and Implications
The relationship between social behavior and brain function is a rich area of study that continues to yield significant insights. Scientists have observed that certain neural circuits, particularly those in the hypothalamus, are responsible for both fulfilling social needs and managing other basic physiological requirements. This dual role illustrates the intricate connections between our biological systems and social interactions. Understanding these connections is crucial for deciphering how impaired social behavior relates to various mental health disorders.
Exploring the neural mechanisms of social behavior opens avenues for addressing the treatment of social deficits associated with mental health conditions. Improved knowledge about how brain activity interacts with social environments can inform therapies that enhance social engagement. By developing strategies to stimulate areas of the brain involved in social behavior, clinicians can help patients reintegrate into social settings and improve their overall well-being. Understanding the nexus between social behavior and brain function could ultimately transform approaches in mental health therapy.
Revisiting Social Needs: A Biological Perspective
The biological perspective on social needs encourages a reevaluation of our understanding of human interactions. Liu’s research posits that the biological drive for social connections might not just derive from a desire for positive feelings but rather stems from an instinct to avoid negative states. This highlights the necessity of understanding social needs through a lens that combines biological imperatives with psychological well-being. Making this connection is vital for public health policy, as it advocates for social engagement as essential for mental health.
By framing social connections as a biological necessity, researchers advocate for proactive strategies to combat social isolation on a community level. This may include promoting social programs and initiatives that foster communal ties and interactions. Ultimately, by acknowledging social needs as fundamental biological components, we can reshape policies and practices that enhance social integration, ensuring a healthier and more connected society.
Insights into Social Behavior Through Animal Models
Animal models, particularly studies involving mice, have provided critical insights into social behavior and its implications for overall health. The researchers’ innovative approach involved examining the neural activity of mice during periods of both deprivation and reunion, which shed light on how social dynamics unfold at a neurological level. Such models are invaluable in understanding the brain’s mechanisms that drive social seeking behavior, providing a foundational framework that can be paralleled to human behavior.
Moreover, findings from animal studies indicate that touch plays a significant role in satisfying social needs. The preference exhibited by mice for tactile stimuli supports the hypothesis that physical interactions are critical to maintaining social bonds, which may also resonate with human experiences. As such, harnessing knowledge from animal behavior can guide future research in developing therapies aimed at mitigating social isolation and promoting healthier social interactions among human populations.
The Role of Touch in Social Connections
Touch is a critical component of social behavior, underscoring the biological and emotional significance of physical interactions in fostering connections. Research has shown that touch can elicit positive emotional responses and enhance feelings of acceptance and belonging. Liu’s conclusions regarding the mice’s preference for tactile experiences after social isolation highlight the importance of this sense in fulfilling social needs. In humans, physical interactions such as hugging, handshaking, and even casual touch can significantly improve relational satisfaction.
Furthermore, as society adapts to increased digital interactions, the role of touch in maintaining social health should not be overlooked. The diminishing opportunities for physical contact may lead to greater feelings of loneliness and disconnection, exacerbating mental health issues. Recognizing the importance of tactile interactions can prompt individuals and communities to seek out ways to incorporate more physical connections, fostering a healthier social environment that supports mental well-being.
Fostering Social Health in the Digital Age
In an era where face-to-face interactions are often supplanted by digital exchanges, fostering social health becomes increasingly critical. Understanding the neurological necessities behind social connections can inform strategies aimed at enhancing interpersonal relationships in a more screen-dominated society. Liu’s insights into social isolation reveal the limitations of virtual communications without real social interactions, making it essential to create environments that promote in-person connectivity and community engagement.
Developing platforms and initiatives that encourage social gatherings, wellness programs, and community-building activities can counteract the isolating effects of technology. By advocating for social health as an integral part of overall well-being, individuals and organizations can collaborate to reshape societal norms around connectivity. This collective effort can help to mitigate feelings of isolation and bolster mental health, demonstrating that even in a digital world, the need for human connection remains fundamental.
The Intersection of Social Connections and Public Health
The relationship between social connections and public health is increasingly recognized as a vital area of concern. The U.S. Surgeon General’s highlighting of social isolation as a public health crisis emphasizes the urgent need to address community well-being through social integration. Research demonstrating the correlation between social connectedness and health outcomes underscores the importance of fostering supportive environments that promote ongoing interpersonal relationships.
Addressing social needs should thus be a core component of public health strategies. By implementing programs that prioritize social wellness alongside traditional health interventions, there is potential to significantly enhance community health outcomes. Recognizing the multifaceted benefits of strong social networks can motivate policy changes that allocate resources toward initiatives that bridge social gaps, showcasing health care that values connection as much as clinical treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the neuroscience of social interaction and why is it important?
The neuroscience of social interaction explores how our brains respond to social cues and stimuli, revealing how social connections are fundamental for mental health. Research highlights that social interactions activate various brain regions, similar to how basic physiological needs like hunger and thirst are regulated, emphasizing their importance in maintaining psychological well-being.
How does social connection influence mental health according to neuroscience?
Neuroscience indicates that strong social connections can significantly enhance mental health by reducing the risk of mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety. Engaging in positive social behaviors triggers the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and oxytocin, which promote feelings of happiness and reduce stress, underscoring the critical role of social connections in emotional resilience.
What are the effects of social isolation on the brain and behavior?
Studies have shown that social isolation can lead to detrimental effects on the brain, causing changes in neural activity and potentially resulting in aversive social behaviors. Prolonged isolation may activate stress responses, leading to increased feelings of loneliness and exacerbating mental health issues, while also altering brain circuitry that governs social behavior.
Why is touch considered significant in the context of social behavior and brain interactions?
Touch is a vital aspect of social behavior, as it engages brain regions responsible for emotional bonding and social signaling. Neuroscience research demonstrates that tactile interactions, such as hugs or handshakes, can enhance feelings of connection and reduce stress, making touch an essential component for fulfilling social needs.
How does the study of social connection neuroscience contribute to understanding psychological needs?
Research in social connection neuroscience aids in comprehending the biological impulses behind human interactions, demonstrating how our brains prioritize social needs akin to physiological needs like food and water. This understanding can inform therapeutic approaches to address mental health issues by fostering social bonds, thus enhancing overall psychological well-being.
What neurological mechanisms underlie the need for social connection?
Neurological mechanisms behind the need for social connection involve specific neural circuits that regulate social behavior much like those controlling hunger and thirst. Studies reveal that activation of certain neurons in the hypothalamus reflects social deprivation, driving individuals to seek social interactions as a way to restore emotional balance and well-being.
In what ways do advancements in understanding the neuroscience of social connections impact public health?
Advancements in understanding the neuroscience of social connections have significant implications for public health, especially in addressing the growing concern of social isolation. By recognizing the vital role of social connections in mental health, healthcare professionals can advocate for community engagement initiatives and support systems, ultimately improving societal mental health outcomes.
Can social behavior and brain chemistry influence each other?
Yes, social behavior and brain chemistry are intricately linked; engaging in social interactions can lead to the release of brain chemicals that foster emotional well-being. Conversely, changes in brain chemistry due to factors like stress or loneliness can impact an individual’s ability or desire to connect socially, underscoring the dynamic interplay between psychology and neuroscience.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection | Considered a fundamental human need, akin to food and shelter. |
| Neurological Basis | Study explores how brain regulates the instinctual need for companionship. |
| Research Findings | Identification of hypothalamic neurons linked to social need fulfilment and the effects of social isolation. |
| Impact of Isolation | Prolonged isolation can lead to aversion to social interaction, similar to hunger. |
| Sensory Inputs | Tactile stimulation is essential for fulfilling social needs; preference shown for physical touch. |
| Human Implications | Insights into how increasing screen interactions affect physical social behaviors. |
| Conclusion from Research | The neural mechanism for social interaction is crucial for understanding mental health. |
Summary
Social connection neuroscience is a fascinating field that uncovers the critical role social interaction plays in human health and wellbeing. This research highlights that social connection is not merely a pleasant experience, but a fundamental need that parallels the necessities of food and water. The insights gained from studying the neurological mechanisms of social behavior underscore the importance of fostering genuine social bonds, especially in an increasingly digital world where physical touch and face-to-face interactions may be diminishing. Understanding these connections can pave the way for better strategies to address mental health issues and enhance overall quality of life.