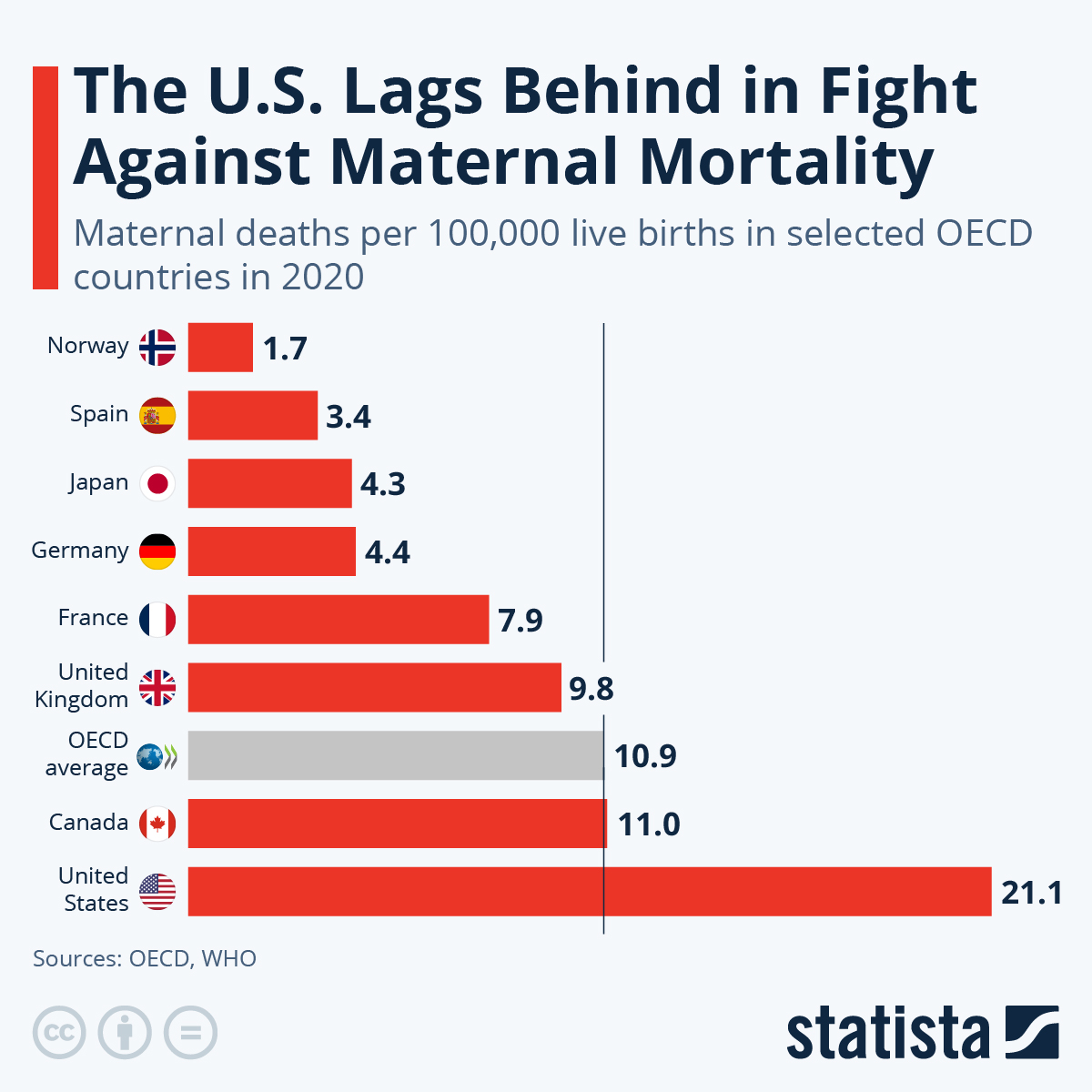
Maternal mortality remains a pressing issue in the U.S., with the country leading high-income nations in pregnancy-related deaths. Alarmingly, studies indicate that over 80% of these fatalities are preventable, highlighting a crucial gap in healthcare provision and access. In recent years, the maternal mortality rate has not only failed to decline but has actually increased, particularly between 2018 and 2022, reflecting persistent disparities among different racial and ethnic groups. The need for improved prenatal and postpartum care is more urgent than ever, as comprehensive care can significantly reduce preventable deaths. As we delve deeper into the factors influencing U.S. maternal health, we must consider the role of ethical healthcare policies and innovations that could lead to meaningful improvements in this area.
The term ‘maternal mortality’ refers to the deaths of women during pregnancy, childbirth, or shortly after, and encompasses a significant public health concern in the United States today. This phenomenon relates closely to issues of pregnancy-related fatalities and the overall maternal health landscape. As we explore the underlying causes of these incidents, it becomes clear that they stem from a complex interplay of various factors, including healthcare access and quality, social inequities, and systemic biases. Emerging discussions around ethical healthcare policies and the necessity for postpartum care improvements are paving the way for better outcomes not just for mothers but for generations to come. By understanding this terminology and its implications, we can foster a more informed dialogue surrounding maternal health initiatives.
Understanding the Rising Maternal Mortality Rates in the U.S.
The United States experiences alarmingly high maternal mortality rates, significantly outpacing other high-income countries. With a maternal mortality rate of 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2022, it is essential to examine the underlying factors contributing to this crisis. Research indicates that over 80 percent of these pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, shedding light on the urgent need for substantial improvements in U.S. maternal health policies. A lack of universal healthcare, persistent healthcare disparities, and uneven access to quality prenatal and postpartum care all contribute to this issue.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention highlights significant disparities in maternal mortality rates across different states and racial groups, making it clear that systemic inequities play a pivotal role. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face mortality rates nearly four times higher than their white counterparts. Addressing racial and regional disparities must be a focus to reduce maternal mortality, necessitating a reassessment of healthcare policies and an investment in effective solutions.
The Role of Ethical Healthcare Policies in Reducing Preventable Deaths
Policymaking plays a crucial role in preventing pregnancy-related deaths, yet the current landscape reveals significant shortcomings. To tackle the steep maternal mortality rates, ethical healthcare policies focused on equitable access to care during pregnancy and postpartum periods are essential. This includes creating comprehensive strategies that address socio-economic factors affecting women’s health. By prioritizing maternal health and demanding accountability from healthcare systems, policymakers can help ensure that all women receive the care they need without facing barriers due to their racial or economic status.
Incorporating ethical principles into healthcare policy can lead to improved outcomes. This involves advocating for policies that not only aim to reduce preventable deaths but also address biases within the healthcare system itself. For instance, reforms could mandate cultural competency training among healthcare providers and include measures to ensure that care is respectful and centered on the patient’s needs and contexts. By creating a healthcare environment that prioritizes ethics and equity, we stand a better chance of significantly lowering the maternal mortality rate.
The Importance of Comprehensive Postpartum Care Improvements
Postpartum care is often overlooked, despite its critical role in ensuring maternal health and preventing pregnancy-related deaths. Recent findings indicate that nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur during the late postpartum period, extending beyond the traditional 42-day timeframe. This underscores the necessity of reshaping the postpartum care approach, promoting continuous support for women long after childbirth. By implementing comprehensive postpartum care plans, healthcare providers can better address emerging health issues in new mothers and help prevent avoidable deaths.
Investing in postpartum care improvements not only supports maternal health but also addresses chronic conditions that may arise during this period. Enhanced follow-ups, access to support groups, and mental health services can significantly impact a woman’s recovery process. As healthcare systems recognize that postpartum care is a long-term journey rather than a brief check-up, there is potential for substantial reductions in maternal mortality rates. This shift will require collaboration among healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities to ensure that mothers receive timely and effective care throughout their recovery.
Addressing Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Maternal Health
Racial and ethnic disparities in maternal health are stark in the United States, with American Indian and Alaska Native women suffering the highest mortality rates. This raises critical questions about systemic injustices and the effectiveness of current healthcare practices. Addressing these disparities involves a multifaceted approach, incorporating community engagement, targeted policy interventions, and awareness campaigns that educate both clients and healthcare professionals about the unique challenges faced by different demographic groups.
To achieve meaningful progress, healthcare systems must commit to dismantling barriers that perpetuate inequality. This includes improving access to culturally sensitive care, ensuring representation within the healthcare workforce, and providing targeted resources to vulnerable populations. By fostering a more inclusive approach to maternal health, we can work towards eliminating the racial and ethnic disparities that have led to increased maternal mortality rates, ultimately ensuring that all women have equal opportunities for safe and healthy pregnancies.
The Impact of Chronic Conditions on Maternal Health
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease have become increasingly common among women of reproductive age, contributing significantly to pregnancy-related fatalities. The shift in leading causes of maternal death from hemorrhages to chronic diseases highlights a pressing need to address these conditions proactively. For effective management, healthcare providers must adopt a holistic view of maternal health that incorporates physical, mental, and social health factors, ensuring comprehensive care before, during, and after pregnancy.
Developing targeted interventions for women with chronic conditions can play a critical role in preventing maternal deaths. These interventions may include regular health screenings, personalized management plans, and early intervention strategies that mitigate the risks associated with chronic diseases during pregnancy. By focusing on preventative measures and chronic condition management, healthcare systems can significantly reduce complications and improve outcomes for mothers and babies alike.
Investing in Public Health Infrastructure as a Solution
To combat the rising maternal mortality rates effectively, significant investment in public health infrastructure is essential. A robust system dedicated to monitoring and addressing maternal health issues can facilitate better data collection, targeted interventions, and resource allocation. This not only helps to track pregnancy-related deaths accurately but also supports informed decision-making at policy levels aimed at improving healthcare access and quality for all pregnant individuals.
Furthermore, bolstering public health infrastructure creates opportunities for community engagement and education. Engaging local communities in awareness programs can help disseminate vital information about maternal health, resources available, and preventive strategies to combat issues like maternal mortality. By ensuring that public health officials have the support and resources needed, we can pave the way for sustainable improvements in maternal health outcomes across the nation.
The Need for Continuous Research in Maternal Health
Continuous research is crucial for understanding and addressing the complexities of maternal mortality. With the landscape of healthcare constantly evolving, including recent challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, ongoing studies are necessary to gather updated data and insights. Investigating the nuances of maternal mortality, especially in the context of changing socio-economic factors and healthcare policies, can equip policymakers with the knowledge necessary to craft effective strategies.
Moreover, research initiatives focusing on both quantitative and qualitative aspects of maternal health can spotlight areas requiring urgent attention. By collaborating with academic institutions, healthcare providers, and community organizations, we can ensure that maternal health research is comprehensive and reflective of the diverse experiences of women across different backgrounds. Essential funding and support for maternal health studies will help to illuminate paths toward significant improvements and foster a healthier future for all mothers.
Encouraging States to Learn from Leading Maternal Health Models
Significant variations in maternal mortality rates across U.S. states indicate the necessity for collaboration and shared learning among healthcare systems. A state like California, which has successfully lowered its maternal mortality rates, can serve as a model for others to emulate. By examining the policies, practices, and innovative solutions implemented in states with better outcomes, we can encourage areas with higher mortality rates to adopt similar strategies.
Collaboration among states could foster a nationwide network dedicated to sharing best practices. This should involve continuous dialogue, data sharing, and mutual accountability to ensure that all states are striving towards equitable maternal health outcomes. Ultimately, learning from successful models not only enhances collective efforts to reduce maternal fatalities but also emphasizes the importance of quality prenatal and postpartum care across the country.
Calling for Comprehensive Policy Reform to Improve Maternal Health Outcomes
Comprehensive policy reform is vital for addressing the persistent challenges in maternal health and reducing preventable deaths. It is crucial to create robust policies that ensure equitable access to quality care, regardless of socio-economic or racial backgrounds. This may include establishing standards for maternal healthcare facilities, increasing funding for maternal health programs, and prioritizing interventions targeting at-risk populations.
In advocating for comprehensive reform, stakeholders must engage with diverse communities to ensure that policies reflect the unique needs and experiences of all women. By emphasizing the importance of inclusion in policymaking, we can develop innovative approaches that align with the goals of improving maternal health outcomes. Ultimately, these reforms will create a healthcare environment that genuinely supports mothers throughout their pregnancy and postpartum journeys, leading to reduced maternal mortality rates.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contribute to the high rate of maternal mortality in the U.S. compared to other high-income countries?
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is influenced by a variety of factors, including a fragmented healthcare system, inequitable access to maternity care, and systemic biases against certain racial and ethnic groups. These issues contribute to higher pregnancy-related deaths and emphasize the need for ethical healthcare policies that ensure equitable care for all mothers.
How many pregnancy-related deaths are preventable in the U.S.?
Research indicates that over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. This highlights the critical need for improvements in maternal health services, including better prenatal care and postpartum care enhancements, to reduce preventable deaths during and after pregnancy.
What improvements are necessary to reduce maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
To effectively reduce maternal mortality rates, it is essential to invest in public health infrastructure, enhance postpartum care, and implement effective policies tailored to address the disparities observed across different states and racial groups. Addressing chronic conditions like hypertension and ensuring comprehensive care can significantly improve outcomes.
Why should late maternal deaths be included in discussions about maternal mortality?
Late maternal deaths, which occur from 42 days to one year postpartum, accounted for nearly one-third of all maternal deaths in the U.S. These deaths are often overlooked, but considering them is vital for improving postpartum care and recognizing that recovery from pregnancy is a longer postpartum continuum than merely the initial six weeks.
What role does racial disparity play in U.S. maternal mortality rates?
Racial disparities profoundly affect U.S. maternal mortality rates, with American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women experiencing significantly higher mortality rates compared to white women. These disparities highlight ongoing inequities in access to quality healthcare and underscore the need for targeted interventions to improve maternal health across all demographics.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted maternal mortality in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted maternal mortality, with a reported increase in rates during 2021. The pandemic exacerbated existing healthcare disparities and may have contributed to worsening maternal health outcomes, emphasizing the need for focused strategies to improve maternal care during such crises.
What are the implications of the findings from the recent studies on maternal mortality in the U.S.?
The findings from recent studies on maternal mortality in the U.S. underline the urgent need for systemic changes in maternal healthcare. With significant rates of preventable deaths and documented disparities across racial groups, there is a critical call for improved healthcare policies, enhanced access to comprehensive care, and a focus on postpartum support.
What are some key chronic conditions affecting maternal mortality in younger women?
Chronic conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease have increasingly affected younger populations, especially those aged 25 to 39. This trend contributes to rising maternal mortality rates and highlights the importance of addressing these conditions through improved maternal health interventions and care practices.
| Key Points |
|---|
| U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries. |
| Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Significant racial disparities exist in maternal mortality rates, particularly among American Indians and Alaska Natives compared to white women. |
| Pregnancy-related death rates increased significantly in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but remained high in 2022. |
| Cardiovascular disease has become the leading cause of pregnancy-related death, surpassing previous causes like hemorrhage. |
| ‘Late maternal deaths,’ those occurring between 42 days and 1 year post-pregnancy, account for nearly one-third of total maternal deaths but are often excluded from mortality definitions. |
| Investment in public health infrastructure and innovative solutions is essential to tackle rising maternal mortality rates and health disparities. |
Summary
Maternal mortality remains a critical issue in the United States, with rates continuing to rise among high-income countries. The alarming statistic that over 80% of these deaths are preventable underscores the urgent need for improved prenatal and postpartum care. Addressing the significant disparities based on race and ethnicity, as well as the alarming trend of increasing cardiovascular-related deaths among pregnant women, is imperative. A comprehensive approach, including better healthcare policies and infrastructure, is essential to reverse the trend in maternal mortality and ensure that all women receive the care they need during and after pregnancy.