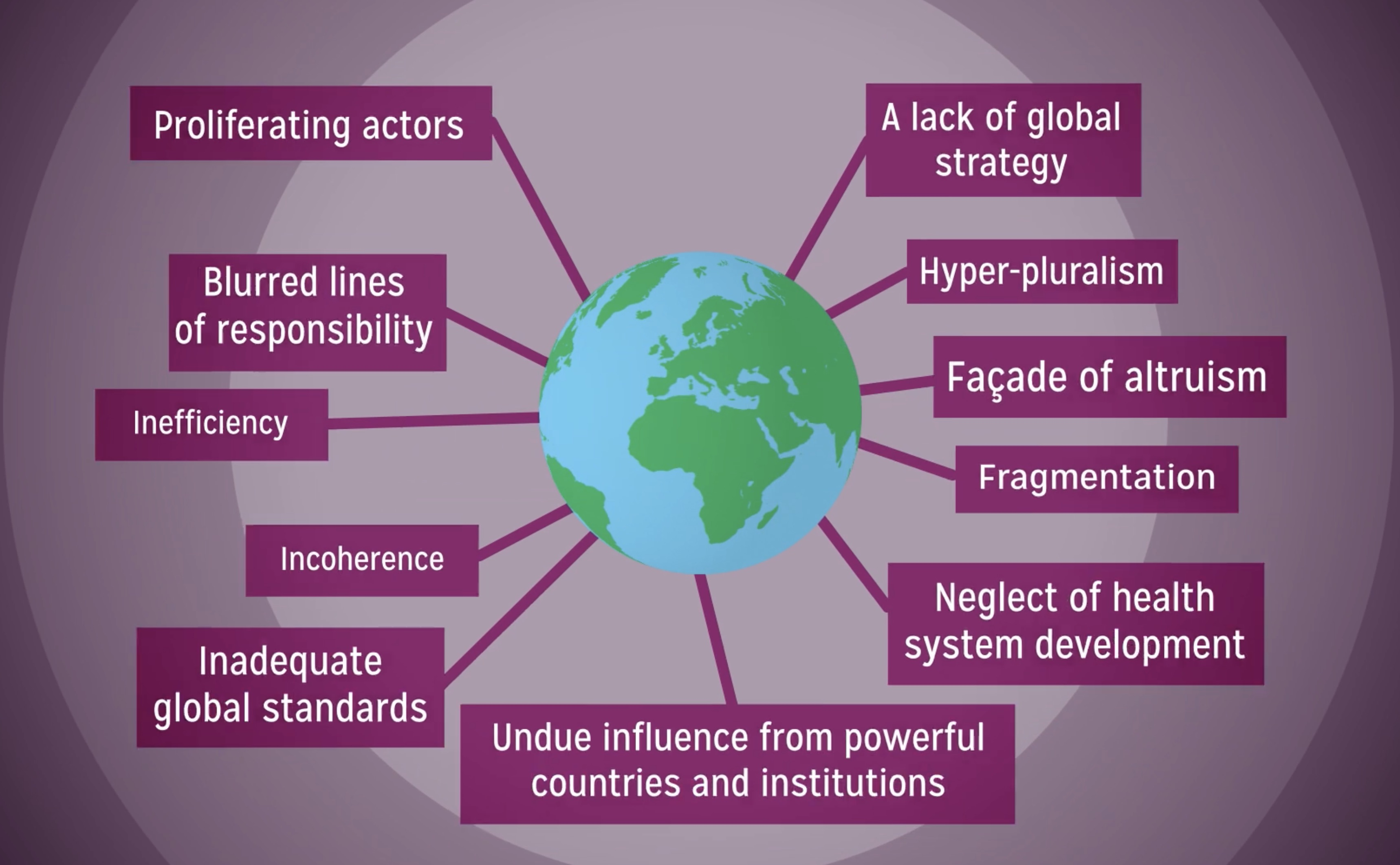
Global health issues have emerged as critical challenges facing humanity today. With the far-reaching impacts of disease outbreaks and the increasing prevalence of chronic conditions, the need for robust public health infrastructure has never been more apparent. As highlighted by renowned physician Atul Gawande and his tenure at USAID, the erosion of global health leadership can have devastating consequences on populations worldwide. Factors such as the dismantling of established health programs not only threaten individual health but also hinder collective progress towards equity in health care access. Addressing these challenges in global health requires a concerted commitment to restoring and strengthening our global health systems, ensuring that every individual, regardless of their location, can achieve better health outcomes.
As we navigate the landscape of international wellness concerns, it is vital to understand the multifaceted nature of health crises affecting populations worldwide. These pressing matters encompass everything from the availability of healthcare resources to the response strategies employed during public health emergencies. Leaders in the field, such as Atul Gawande, emphasize the importance of sustained efforts in restoring health initiatives that have faced cuts in funding and support. The challenges posed by these global health dynamics demand innovative solutions and a strategic approach to enhance our healthcare capabilities. Ultimately, our ability to mitigate health disparities relies on strong international collaboration and the commitment to reinvigorate health systems across the globe.
The Impact of USAID on Global Health
USAID has historically played a pivotal role in advancing global health initiatives, funding programs that address diseases and improve healthcare access in developing nations. As Atul Gawande pointed out, during its prime, USAID helped build a vast network of surveillance for deadly outbreaks, significantly reducing response times to public health crises such as Ebola and H1N1. This agency not only provided immediate relief but also established long-term health infrastructure that many countries still rely on today.
The dismantling of USAID under recent administrations has raised alarms within the public health community. Gawande noted that the drastic cuts to staff and funding have resulted in setbacks for millions, particularly in efforts to combat maternal mortality and improve child health. Such challenges in global health demand urgent attention; without agencies like USAID actively leading initiatives, the progress made over decades could regress, leaving vulnerable populations without necessary resources.
Challenges in Restoring Public Health Infrastructure
Restoring the public health infrastructure dismantled in recent years poses a monumental challenge. Gawande emphasized that the scars left on the healthcare system after severe budget cuts cannot be easily healed. Programs that once ensured maternal and child health, infection prevention, and essential medications have suffered considerably, threatening to reverse the advancements made in global health outcomes. To rebuild, there needs to be a strategic investment in personnel and programs that prioritize health equity and accessible care.
Moreover, the ongoing freeze in funding for research initiatives, such as those at Ariadne Labs founded by Gawande, has further complicated recovery efforts. Innovative solutions require sustained support, and it is essential that investments in research and development are incrementally reinstated. Reviving collaborations between government entities and academic institutions will be vital to re-establish the trust and effectiveness needed to overcome the public health crises that loom on the horizon.
The Role of Global Health Leadership
Global health leadership is crucial in navigating the complex challenges that arise within health initiatives worldwide. With American leadership in global health facing uncertainty, Gawande highlighted the possibility that other nations may rise to fill this void. This shift necessitates a reevaluation of how developed countries engage with global health issues, especially given the interconnectedness of health systems across borders. Countries must collaborate to harness shared knowledge and address pressing health disparities.
Strong global health leadership is also about empowering local communities to take ownership of their health outcomes. Encouraging local solutions and initiatives that resonate with the unique challenges faced by different communities is essential. This approach ensures that interventions are culturally relevant and sustainable, ultimately leading to enhanced health outcomes. As emerging leaders in this space, the next generation of health professionals must be equipped with the skills and knowledge needed to foster such collaborative efforts.
The Future of Public Health Advocacy
Public health advocacy remains a cornerstone of successful global health efforts. Gawande’s reflections on the importance of ongoing support for health infrastructure signal a need for a collective rebirth of advocacy movements that promote awareness and action against public health challenges. Through strengthening connections between policymakers, healthcare providers, and communities, advocates can mobilize resources and call for necessary reforms that prioritize health access for all.
Additionally, leveraging social media and technology to amplify public health messages can have a profound impact. In an increasingly digital world, utilizing platforms to engage populations and advocate for effective health policies can drive momentum for change. It’s imperative that advocates harness these tools not only to raise awareness but also to mobilize action against health inequities, with a focus on sustainability and long-term impacts.
Strengthening International Health Partnerships
International health partnerships are integral to enhancing health systems globally, particularly in resource-limited settings. Gawande’s insights into USAID’s collaborative efforts with various organizations showcase how shared expertise and resources lead to effective health interventions. Strengthening these partnerships can foster innovation, improve access to healthcare, and ultimately save lives, underscoring the importance of collective action in health initiatives.
However, rebuilding these partnerships requires a clear commitment from both domestic and international stakeholders. The challenge of recent funding cuts highlights the necessity for a renewed focus on sustained cooperation between countries, NGOs, and public health entities. By aligning priorities and pooling resources, stakeholders can address not only immediate health challenges but also foster resilience against future public health emergencies.
The Importance of Scientific Integrity in Health Initiatives
Gawande’s return to academia amidst attacks on research funding illustrates the fragility of scientific integrity in health initiatives. Ensuring that health policies are rooted in empirical evidence is vital for effectively addressing health issues on a global scale. Upholding the integrity of research institutions is critical, as it directly impacts their ability to contribute valuable insights that can inform and improve public health strategies.
This commitment to scientific integrity also encompasses transparency and accountability within health systems. Engaging diverse stakeholders in policymaking processes enhances trust and fosters environments where science can thrive. Ultimately, prioritizing rigorous science-backed initiatives builds a foundation for effective health solutions and strengthens public confidence in healthcare systems.
Lessons from Global Health Crises
Drawing lessons from past global health crises is essential for preparing for future challenges. Gawande referenced successes and failures during his tenure with USAID, demonstrating the need for agility and responsiveness in health frameworks. Historical insights into outbreak responses can guide contemporary strategies, ensuring that lessons learned are applied to future public health emergencies.
Moreover, fostering a culture of continuous learning within global health organizations can bridge gaps between policy and practice. A proactive approach that prioritizes adaptive management and resilience will form more robust responses to emerging health threats. By synthesizing these lessons, global health leaders can better position themselves to navigate the complexities of public health on a worldwide scale.
Empowering Future Public Health Professionals
The next generation of public health professionals stands at the forefront of addressing global health challenges. Gawande emphasized the importance of nurturing talent within the field, ensuring that emerging leaders are equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary to drive impactful health initiatives. Education and training programs must adapt to include interdisciplinary approaches, addressing the multifaceted nature of health challenges.
Furthermore, opportunities for hands-on experience through internships and fieldwork can greatly enrich educational trajectories. Engaging students in real-world scenarios fosters a sense of responsibility and commitment to health advocacy, vital for promoting health equity globally. It is imperative that academic institutions empower future public health leaders to act with the conviction and adaptability required to reshape the landscape of global health.
Public Health Policy Reforms for Future Resilience
Reforming public health policies is critical for ensuring resilience against future health crises. Gawande noted that systemic changes are needed to enhance the functionality of health systems, especially in a post-pandemic world. Such reforms must focus on improving access to care, bolstering funding for health research, and incorporating feedback from frontline healthcare workers who understand the nuances of existing systems.
Moreover, policy reforms must incorporate a holistic understanding of social determinants of health. By addressing factors like poverty, education, and environment, public health policies can foster a more equitable healthcare landscape. Stakeholders must work collaboratively to advocate for policies that address these determinants, ensuring a more just and healthy future for all populations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the significant challenges in global health today?
Significant challenges in global health today include the impact of disrupted public health infrastructures, the rise of infectious diseases, and access to healthcare resources. The dismantling of agencies like USAID has intensified these issues, notably by reducing funding for global health initiatives that have been critical in combating diseases such as HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria.
How does USAID impact global health leadership?
USAID plays a crucial role in global health leadership by funding and supporting health programs worldwide. It enables countries to build effective public health infrastructures and establish rapid response systems for infectious diseases. The agency’s ability to respond to global health challenges, as highlighted by Atul Gawande, has been severely affected by recent cuts, jeopardizing health outcomes in several nations.
What role did Atul Gawande play at USAID in improving global health?
Atul Gawande served as the head of USAID’s Bureau for Global Health, where he focused on strengthening health systems and enhancing responses to global health crises. His leadership aimed to reduce maternal and childhood mortality and improve healthcare delivery in over 50 countries, significantly impacting global health outcomes.
How can public health infrastructure be improved to address global health issues?
Improving public health infrastructure requires increased funding, training for health professionals, and effective partnerships among governments, NGOs, and the private sector. Support from organizations like USAID is vital to ensure that countries can implement comprehensive health strategies that lead to sustainable improvements in health outcomes.
What strategies can be employed to address the challenges in global health identified by Atul Gawande?
Strategies to address global health challenges include enhancing surveillance systems for infectious diseases, maintaining funding for crucial health programs, and fostering international collaborations. These approaches can help mitigate the impact of health crises and strengthen global health security.
Why is America’s role in global health leadership important?
America’s role in global health leadership is crucial because it provides essential resources, expertise, and collaboration necessary for effectively combating diseases worldwide. As noted by Atul Gawande, if the U.S. retreats from this role, it may hinder progress in global health initiatives and allow other nations to fill the void, potentially shifting the landscape of global health responses.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Impact of USAID Cuts | The cuts led to nearly all staff being fired and 85% of programs terminated, devastating global health efforts. |
| Gawande’s Role at USAID | Atul Gawande led USAID’s Bureau for Global Health, significantly impacting health programs across 50 countries. |
| Health Program Achievements | USAID’s efforts improved global response to diseases, reduced maternal mortality, and treated HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria. |
| Research Funding Freeze | Federal funding cuts, including Harvard research, threaten advancements in health and science. |
| Optimism for Global Health | Despite challenges, Gawande remains hopeful that global health can progress with new leaders emerging. |
Summary
Global health issues have come into sharp focus due to the recent cuts to the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), which has severely hindered essential programs. Atul Gawande emphasizes the devastating effects of these reductions, noting the loss of vital health infrastructure and staff, which jeopardizes health outcomes worldwide. However, he encourages future leaders in health to remain committed to advancing science and improving health systems, highlighting the importance of resilience and innovation in overcoming these challenges.